What Is 1 4 Times 3
sonusaeterna
Dec 06, 2025 · 10 min read
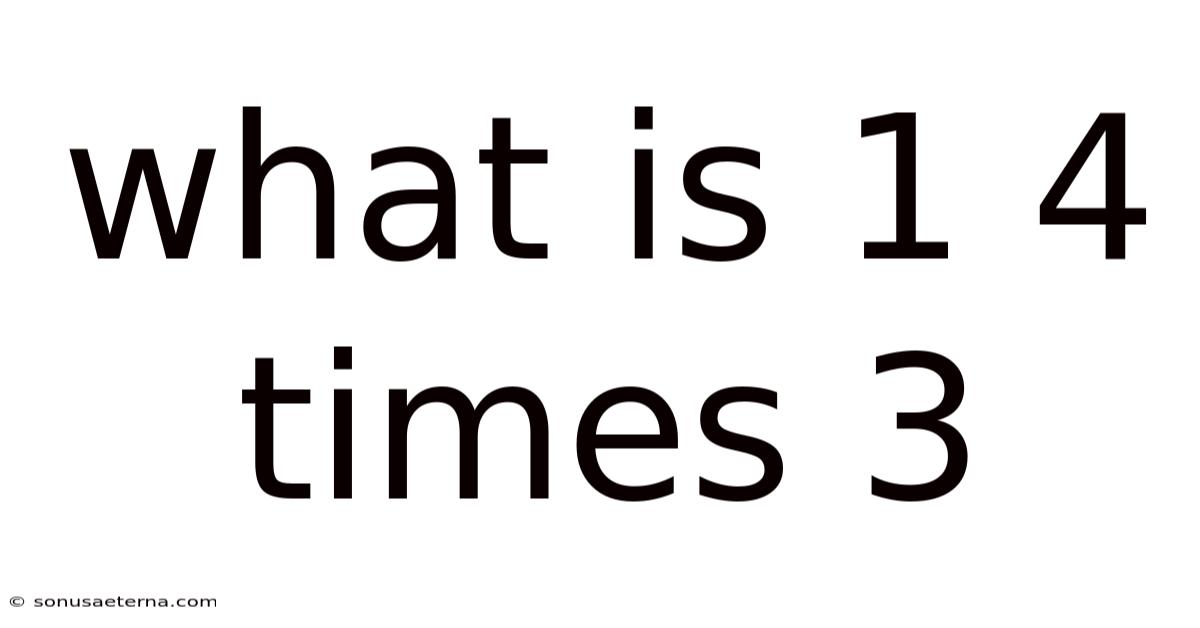
Table of Contents
Imagine you're baking a cake, and the recipe calls for multiplying ingredients in unusual ways. Or perhaps you're planning a garden and need to calculate the exact amount of fertilizer. These everyday scenarios often require us to do more than just simple arithmetic. Multiplying mixed numbers and whole numbers, like figuring out what 1 ¼ times 3 is, might seem a little daunting at first, but with the right approach, it becomes a straightforward and useful skill.
Think about how often you encounter fractions in real life. From splitting a pizza to measuring fabric for a sewing project, fractions are everywhere. Now, consider situations where you need to scale something up or down—like tripling a recipe or halving the amount of paint needed for a room. That's where multiplying mixed numbers comes in handy. Understanding how to calculate 1 ¼ times 3 isn't just an abstract math problem; it's a practical tool that can simplify many of your daily activities.
Decoding 1 ¼ Times 3: A Comprehensive Guide
At its core, understanding "1 ¼ times 3" involves grasping how to multiply a mixed number (1 ¼) by a whole number (3). This seemingly simple operation combines basic multiplication with an understanding of fractions, offering a foundational skill applicable in numerous real-world scenarios. Whether you're a student brushing up on your math skills or someone looking to apply practical math in everyday situations, mastering this calculation is incredibly useful.
To truly understand this, we'll break down the concept into digestible parts. We will look into the definitions of mixed numbers and how they differ from other types of numbers, and explore the fundamental principles of multiplying fractions. This foundational knowledge will empower you to confidently tackle calculations like "1 ¼ times 3" and more complex problems.
Comprehensive Overview
Understanding Mixed Numbers
A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. For example, 1 ¼ is a mixed number where 1 is the whole number and ¼ is the fractional part. Mixed numbers provide a convenient way to represent quantities that are greater than one but not a whole number themselves.
Proper fractions, on the other hand, are fractions where the numerator (the top number) is less than the denominator (the bottom number), such as ¼, ½, or ¾. When the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator, it's called an improper fraction, like 5/4.
The ability to convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions is fundamental to performing arithmetic operations like multiplication. To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction, you multiply the whole number by the denominator of the fraction, add the numerator, and then place the result over the original denominator. For example, to convert 1 ¼ to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number (1) by the denominator (4): 1 x 4 = 4
- Add the numerator (1) to the result: 4 + 1 = 5
- Place the sum over the original denominator (4): 5/4
Therefore, 1 ¼ is equivalent to 5/4.
Principles of Multiplying Fractions
Multiplying fractions involves a straightforward process: you multiply the numerators together to get the new numerator, and you multiply the denominators together to get the new denominator. Mathematically, if you have two fractions a/b and c/d, their product is (a x c) / (b x d).
For example, let's multiply ½ by ¾:
- Multiply the numerators: 1 x 3 = 3
- Multiply the denominators: 2 x 4 = 8
- The result is 3/8
When multiplying a fraction by a whole number, you can think of the whole number as a fraction with a denominator of 1. For example, multiplying ½ by 3 is the same as multiplying ½ by 3/1. Applying the rule:
- Multiply the numerators: 1 x 3 = 3
- Multiply the denominators: 2 x 1 = 2
- The result is 3/2
The fraction 3/2 is an improper fraction, which can be converted back into a mixed number. To do this, divide the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number, the remainder becomes the new numerator, and the denominator stays the same:
- 3 ÷ 2 = 1 with a remainder of 1, so 3/2 = 1 ½
Step-by-Step Calculation of 1 ¼ Times 3
Now, let's apply these principles to calculate 1 ¼ times 3.
Step 1: Convert the Mixed Number to an Improper Fraction
As shown earlier, 1 ¼ is equivalent to 5/4. This conversion is crucial because it simplifies the multiplication process.
Step 2: Express the Whole Number as a Fraction
The whole number 3 can be expressed as the fraction 3/1.
Step 3: Multiply the Fractions
Now, multiply 5/4 by 3/1:
- Multiply the numerators: 5 x 3 = 15
- Multiply the denominators: 4 x 1 = 4
- The result is 15/4
Step 4: Convert the Improper Fraction Back to a Mixed Number
Convert the improper fraction 15/4 back to a mixed number:
- 15 ÷ 4 = 3 with a remainder of 3, so 15/4 = 3 ¾
Therefore, 1 ¼ times 3 is equal to 3 ¾.
Alternative Method: Distributive Property
Another way to approach this problem is by using the distributive property of multiplication over addition. This method can be particularly useful for those who find it easier to work with whole numbers and fractions separately.
Step 1: Break Down the Mixed Number
Separate the mixed number 1 ¼ into its whole number and fractional parts: 1 + ¼.
Step 2: Apply the Distributive Property
Multiply both the whole number and the fraction by 3:
- (1 x 3) + (¼ x 3)
Step 3: Perform the Multiplication
- 1 x 3 = 3
- ¼ x 3 = ¾
Step 4: Add the Results
Add the two results together:
- 3 + ¾ = 3 ¾
Again, we find that 1 ¼ times 3 is equal to 3 ¾. This method offers an alternative way to visualize and solve the problem, which can be especially helpful for those who prefer to avoid converting mixed numbers to improper fractions.
Trends and Latest Developments
In today's educational landscape, there's a growing emphasis on practical math skills. Educators are increasingly focusing on real-world applications of mathematical concepts, and multiplying fractions and mixed numbers is a key area. Recent trends in math education highlight the importance of conceptual understanding over rote memorization, encouraging students to explore multiple methods to solve problems, like the two approaches we discussed above.
According to educational research, students who understand the underlying principles of mathematical operations are more likely to retain the knowledge and apply it effectively in various contexts. This understanding is fostered through interactive activities, visual aids, and problem-solving tasks that mimic real-life scenarios. For instance, teachers might use cooking recipes or construction projects to illustrate the use of fractions and mixed numbers in practical situations.
Furthermore, the integration of technology in math education has provided new tools and resources for teaching and learning these concepts. Online platforms and educational apps offer interactive simulations, personalized learning paths, and immediate feedback, making it easier for students to grasp and practice multiplying mixed numbers.
Tips and Expert Advice
Master the Basics
Before tackling more complex problems, ensure you have a solid understanding of basic multiplication and fraction concepts. This includes knowing your multiplication tables, understanding equivalent fractions, and being comfortable with converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions.
Why it's important: A strong foundation in these areas will make it easier to understand the more advanced concepts and reduce the likelihood of making mistakes.
How to do it: Practice multiplication tables regularly, use visual aids to understand fractions, and work through simple conversion exercises.
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, proficiency in multiplying mixed numbers comes with practice. Regular practice not only reinforces the concepts but also helps you develop speed and accuracy.
Why it's important: Consistent practice helps you internalize the steps involved and develop a sense of intuition for solving these problems.
How to do it: Dedicate a few minutes each day to solving multiplication problems involving fractions and mixed numbers. Use online resources, textbooks, or create your own practice problems.
Use Visual Aids
Visual aids can be incredibly helpful in understanding and solving fraction problems. Diagrams, number lines, and pie charts can make abstract concepts more concrete and easier to grasp.
Why it's important: Visual aids provide a visual representation of the problem, which can help you understand the relationships between numbers and fractions.
How to do it: Draw diagrams to represent fractions, use number lines to visualize multiplication, and use pie charts to understand proportions.
Break Down Complex Problems
When faced with a complex problem, break it down into smaller, more manageable steps. This approach makes the problem less intimidating and easier to solve.
Why it's important: Breaking down a problem into smaller steps allows you to focus on one aspect at a time, reducing the cognitive load and making it easier to avoid errors.
How to do it: Identify the different steps involved in the problem, such as converting mixed numbers, multiplying fractions, and simplifying the result. Address each step individually.
Double-Check Your Work
Always double-check your work to ensure accuracy. Mistakes can easily happen, especially when dealing with fractions and mixed numbers.
Why it's important: Double-checking your work can help you catch and correct errors before they become significant problems.
How to do it: Review each step of your calculation, paying close attention to conversions, multiplication, and simplification. If possible, use a calculator or online tool to verify your answer.
Apply Real-World Scenarios
Applying mathematical concepts to real-world scenarios can make learning more engaging and relevant. Look for opportunities to use fractions and mixed numbers in everyday situations, such as cooking, measuring, or budgeting.
Why it's important: Applying math to real-world scenarios helps you understand the practical applications of the concepts and reinforces your learning.
How to do it: When cooking, adjust recipe quantities using fractions. When measuring, use fractions to calculate lengths or areas. When budgeting, use fractions to allocate funds.
FAQ
Q: What is a mixed number?
A: A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction, such as 1 ¼ or 2 ½. It represents a quantity greater than one.
Q: How do I convert a mixed number to an improper fraction?
A: Multiply the whole number by the denominator of the fraction, add the numerator, and place the result over the original denominator. For example, 2 ½ = (2 x 2 + 1) / 2 = 5/2.
Q: Can I use a calculator to multiply mixed numbers?
A: Yes, many calculators can handle mixed number calculations. However, understanding the underlying principles is essential for problem-solving.
Q: Why is it important to convert mixed numbers to improper fractions before multiplying?
A: Converting to improper fractions simplifies the multiplication process by allowing you to multiply the numerators and denominators directly.
Q: What if I need to multiply more than two fractions or mixed numbers?
A: The same principles apply. Convert any mixed numbers to improper fractions, then multiply all the numerators together and all the denominators together.
Conclusion
In summary, calculating 1 ¼ times 3 involves converting the mixed number to an improper fraction, multiplying it by the whole number (expressed as a fraction), and simplifying the result back to a mixed number if necessary. The answer, as we've demonstrated through multiple methods, is 3 ¾. This exercise not only reinforces basic mathematical principles but also highlights the practical applications of fractions in everyday life.
Now that you've grasped the fundamentals of multiplying mixed numbers, why not put your skills to the test? Try solving similar problems, explore more complex calculations, and challenge yourself to find real-world scenarios where you can apply this knowledge. Share your experiences, ask questions, and continue honing your mathematical abilities. Happy calculating!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Elements In Groups 3 12 On Periodic Table
Dec 06, 2025
-
How Did The Comanche Get Their Food
Dec 06, 2025
-
What Planes Are The Blue Angels
Dec 06, 2025
-
8 5 Cm Is How Many Inches
Dec 06, 2025
-
What Is 1 4 Times 3
Dec 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 1 4 Times 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.