What Is 50 C In F
sonusaeterna
Nov 17, 2025 · 10 min read
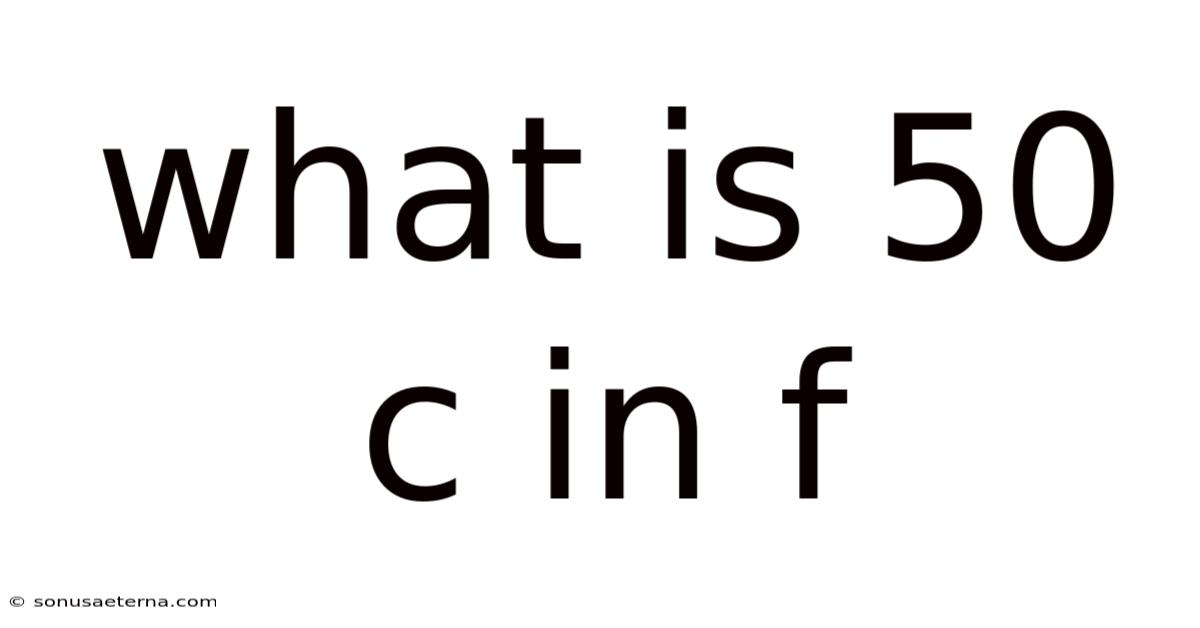
Table of Contents
The question "What is 50 C in F?" is a common one, especially for those who frequently encounter temperature scales in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. Temperature conversion is essential in many fields, including science, cooking, meteorology, and international travel. Understanding how to convert between these two scales allows for better comprehension and application of temperature-related data.
The need to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit arises from the fact that different regions and disciplines use different temperature scales. While most of the world uses Celsius (°C), the United States and a few other countries still predominantly use Fahrenheit (°F). This discrepancy can lead to confusion when interpreting weather reports, cooking instructions, or scientific data. Knowing how to accurately convert between the two scales ensures you can understand and use the information effectively, regardless of the scale in which it is presented. Converting 50°C to Fahrenheit specifically helps bridge this gap, providing a clear understanding of this temperature in a Fahrenheit context.
Main Subheading
To fully grasp the process of converting Celsius to Fahrenheit, it's important to understand the background and context of these temperature scales. Celsius, also known as centigrade, is part of the metric system and is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Zero degrees Celsius (0°C) is the freezing point of water, and 100 degrees Celsius (100°C) is the boiling point. This scale is widely used in scientific applications due to its simplicity and direct relationship to water's physical properties. Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, originally proposed a reversed version of this scale in 1742, but it was later inverted to its current form.
Fahrenheit, on the other hand, is based on a scale originally defined by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. In this scale, 32 degrees Fahrenheit (32°F) is the freezing point of water, and 212 degrees Fahrenheit (212°F) is the boiling point. The Fahrenheit scale was initially based on the freezing point of a brine solution (a mixture of water, ice, and salt) and the human body temperature. Although the Fahrenheit scale is still used in some countries, it is less common in scientific contexts because it is not as directly related to fundamental physical properties as Celsius. The United States continues to use Fahrenheit in everyday applications, which is why understanding the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit remains important.
Comprehensive Overview
The conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit involves a specific formula that takes into account the different reference points and scale increments of the two systems. The formula to convert Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F) is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This formula adjusts for the fact that the Celsius scale has 100 degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water, while the Fahrenheit scale has 180 degrees (212 - 32 = 180). The 9/5 factor accounts for this difference in scale, and the addition of 32 accounts for the offset in the freezing points.
Detailed Steps for Conversion
To convert 50°C to Fahrenheit, follow these steps:
-
Multiply by 9/5:
Multiply 50°C by 9/5 (which is equivalent to 1.8):
50 × 1.8 = 90
-
Add 32:
Add 32 to the result:
90 + 32 = 122
Therefore, 50°C is equal to 122°F. This calculation provides a precise conversion, ensuring accuracy in applications ranging from cooking to scientific experiments.
History and Evolution of Temperature Scales
The development of temperature scales has a rich history, dating back to early attempts to quantify hotness and coldness. Before standardized scales, people relied on subjective assessments, which were unreliable and inconsistent. The creation of the Fahrenheit scale by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century marked a significant step forward. Fahrenheit initially used a mercury-in-glass thermometer and defined his scale based on the freezing point of a brine solution and human body temperature.
Later, Anders Celsius proposed the Celsius scale, which was initially a reversed scale. It was later inverted to the form we use today, with 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as the boiling point. The Celsius scale gained popularity due to its simplicity and relationship to the physical properties of water, making it particularly useful in scientific applications.
Over time, the Celsius scale became part of the metric system and was adopted by most countries around the world. The Fahrenheit scale, however, remained in use in the United States and a few other countries. This divergence has led to the ongoing need for temperature conversion, particularly in international contexts and scientific collaborations.
Significance of Accurate Temperature Conversion
Accurate temperature conversion is critical in various fields. In cooking, precise temperatures are essential for achieving desired results, such as baking the perfect cake or roasting meat to the correct doneness. In scientific research, temperature accuracy is crucial for experiments and data analysis, as temperature can significantly affect chemical reactions and physical properties.
In meteorology, understanding temperature in both Celsius and Fahrenheit is necessary for communicating weather information to a diverse audience. International travelers also benefit from knowing how to convert temperatures, as they may encounter different scales in different countries. Furthermore, in industries such as pharmaceuticals and manufacturing, temperature control is vital for maintaining product quality and safety.
Comparison with Other Temperature Scales
While Celsius and Fahrenheit are the most commonly used temperature scales, other scales exist, such as Kelvin and Rankine. The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale used primarily in scientific contexts. Zero Kelvin (0 K) is absolute zero, the point at which all molecular motion ceases. The Kelvin scale is related to Celsius by the formula:
K = °C + 273.15
The Rankine scale is an absolute temperature scale similar to Kelvin but uses Fahrenheit degrees. Zero Rankine (0 °R) is absolute zero, and the scale is related to Fahrenheit by the formula:
°R = °F + 459.67
Understanding these different temperature scales and how they relate to each other provides a comprehensive view of temperature measurement and its applications in various fields.
Trends and Latest Developments
In recent years, there has been a growing trend toward the standardization of temperature scales, particularly in scientific and international contexts. The Celsius scale is increasingly recognized as the standard for scientific research, and many countries that historically used Fahrenheit are gradually adopting Celsius for everyday use. This shift is driven by the need for consistency and accuracy in global communication and collaboration.
Data and Popular Opinions
Data from various sources indicate that the majority of the world's population uses Celsius as their primary temperature scale. This preference is reflected in scientific publications, international standards, and weather reporting in most countries. However, popular opinion in the United States remains divided, with many people still preferring Fahrenheit for everyday use.
Professional insights suggest that while the transition to Celsius may take time in some regions, the long-term trend is toward greater standardization. This trend is supported by the increasing use of metric units in various industries and the growing recognition of the benefits of a unified temperature scale for global communication and collaboration.
Impact of Technology on Temperature Measurement
Advancements in technology have also played a significant role in temperature measurement. Digital thermometers and sensors have become more accurate and affordable, making it easier to measure and convert temperatures in real time. These tools are widely used in various applications, from cooking and healthcare to industrial processes and environmental monitoring.
Moreover, online converters and mobile apps have made it simple for anyone to quickly convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit. These resources are particularly useful for travelers, students, and professionals who need to work with different temperature scales on a regular basis. The availability of these tools has further facilitated the understanding and use of temperature data in various contexts.
Tips and Expert Advice
Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit can be made even easier with a few practical tips and expert advice. These strategies can help you quickly estimate temperatures and avoid common mistakes.
Mental Math Techniques
One useful tip is to use mental math techniques to approximate the conversion. For example, to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit in your head, you can double the Celsius value, subtract 10% of that doubled value, and then add 32. This method provides a reasonable estimate, especially for everyday situations where precise accuracy is not critical.
For example, to estimate 50°C in Fahrenheit:
- Double 50: 50 × 2 = 100
- Subtract 10%: 100 - 10 = 90
- Add 32: 90 + 32 = 122
This mental calculation yields 122°F, which is the exact conversion.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One common mistake is to forget the order of operations in the conversion formula. It is essential to first multiply the Celsius value by 9/5 (or 1.8) and then add 32. Failing to follow this order can lead to significant errors in the conversion.
Another mistake is to confuse the two scales and accidentally apply the wrong formula. It is crucial to remember that to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, you multiply by 9/5 and add 32, while to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, you subtract 32 and multiply by 5/9.
Using Online Converters and Apps
For precise conversions, online converters and mobile apps are invaluable tools. These resources eliminate the risk of manual calculation errors and provide accurate results in seconds. Many websites and apps offer additional features, such as the ability to convert between multiple temperature scales and save frequently used conversions.
When using online converters, it is important to ensure that the tool is reliable and accurate. Look for converters that are recommended by reputable sources or used by professionals in relevant fields. Additionally, double-check the results to ensure that they are reasonable and consistent with your understanding of the temperature scales.
Practical Examples
Consider these practical examples to illustrate the importance of accurate temperature conversion:
-
Cooking: A recipe calls for baking a cake at 180°C. To use this recipe in the United States, you need to convert this temperature to Fahrenheit:
°F = (180 × 9/5) + 32 = 356°F
-
Weather Reporting: A weather forecast predicts a high of 30°C. To understand this temperature in Fahrenheit:
°F = (30 × 9/5) + 32 = 86°F
-
Scientific Experiment: A chemical reaction needs to be conducted at 25°C. To convert this temperature to Fahrenheit:
°F = (25 × 9/5) + 32 = 77°F
By understanding and applying these conversion techniques, you can confidently work with temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, regardless of the context.
FAQ
Q: What is the formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A: The formula is °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32.
Q: Why do some countries use Fahrenheit while others use Celsius?
A: The use of Fahrenheit in the United States is largely historical, while most other countries have adopted Celsius as part of the metric system.
Q: Is there a quick way to estimate Celsius to Fahrenheit in my head?
A: Yes, double the Celsius value, subtract 10% of the doubled value, and add 32.
Q: What is 0 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit?
A: 0°C is equal to 32°F.
Q: Why is accurate temperature conversion important?
A: Accurate conversion is crucial in cooking, science, meteorology, and international travel to ensure correct application and understanding of temperature data.
Conclusion
In summary, converting 50°C to Fahrenheit involves using the formula °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32, which results in 122°F. Understanding this conversion is essential for various applications, from cooking and weather reporting to scientific research and international communication. Knowing the history, trends, and practical tips related to temperature conversion enhances your ability to work with different temperature scales confidently.
Now that you understand how to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, take the next step and practice converting other temperatures. Use online converters or mental math techniques to improve your skills and ensure accuracy in your daily life. Share this knowledge with others and help bridge the gap between Celsius and Fahrenheit users worldwide.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Return On Total Assets
Nov 17, 2025
-
Difference Between Past Participle And Past Tense
Nov 17, 2025
-
Symptoms Of Dislocated Rib In Back
Nov 17, 2025
-
How Many Grams Are In One Pound
Nov 17, 2025
-
Who Played An Important Role In American Revolution
Nov 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 50 C In F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.