85 Degrees F Is What C
sonusaeterna
Dec 05, 2025 · 11 min read
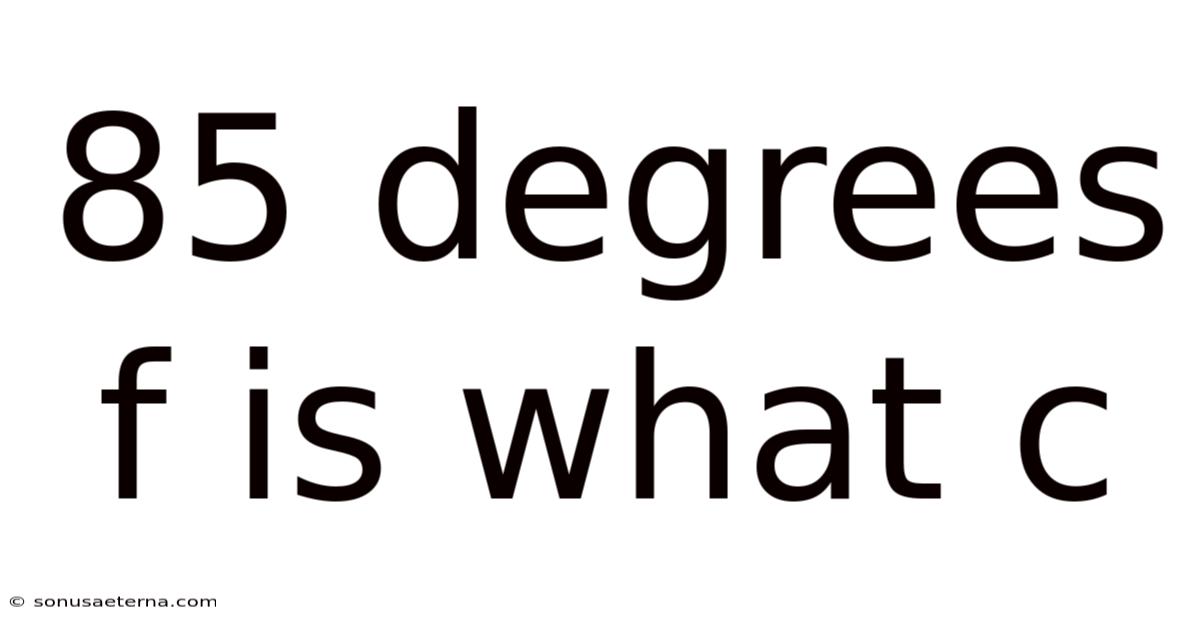
Table of Contents
The sun beats down, the air shimmers, and you reach for a cool drink. You hear someone mention it's 85 degrees Fahrenheit outside, and you instinctively know it's warm. But what if you're talking to someone who uses Celsius? How do you translate that familiar warmth into a universally understood number? Understanding temperature conversions, especially from Fahrenheit to Celsius, is more than just a matter of convenience; it's a bridge that connects different perspectives and systems of measurement across the globe.
Imagine you're planning a trip to Europe, where Celsius reigns supreme. You meticulously check the weather forecast, only to be greeted with a string of unfamiliar numbers. What does 29 degrees Celsius even feel like? The ability to quickly convert temperatures becomes essential for packing appropriately, planning outdoor activities, and generally understanding your environment. This article will not only provide you with the simple formula to convert 85 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius but will also delve into the history, science, and practical applications of temperature scales.
Main Subheading
Temperature is a fundamental physical quantity that measures the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. In simpler terms, it tells us how hot or cold something is. But the way we quantify this "hotness" or "coldness" varies across the world. While the United States relies heavily on the Fahrenheit scale, most other countries use Celsius. This difference stems from historical and scientific choices, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding the relationship between Fahrenheit and Celsius is crucial for international communication, scientific endeavors, and even everyday tasks like cooking and traveling. While there are numerous online converters and calculators available, knowing the underlying formula and the context behind these scales empowers you to make informed decisions and truly grasp the temperatures you encounter. Let's explore the world of temperature scales and unlock the secrets of converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius.
Comprehensive Overview
To truly appreciate the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius, it's essential to understand the origins and definitions of each scale. Both scales were developed independently, based on different reference points and approaches to dividing the range of temperatures.
Fahrenheit: Developed by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, the Fahrenheit scale was initially based on two reference points: 0 degrees Fahrenheit was the temperature of a brine solution (a mixture of water, ice, and salt), and 96 degrees Fahrenheit was approximately the normal human body temperature. Fahrenheit chose these somewhat arbitrary points to create a scale with finer gradations, believing it would allow for more precise measurements. Later, the scale was redefined to use the freezing point of water (32°F) and the boiling point of water (212°F) as fixed points, maintaining the 180-degree interval between them.
Celsius: Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, proposed the Celsius scale in 1742. Originally, Celsius's scale was inverted, with 0 degrees representing the boiling point of water and 100 degrees representing the freezing point. Jean-Pierre Christin later reversed the scale to its current form, where 0 degrees Celsius is the freezing point of water and 100 degrees Celsius is the boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure. This decimal-based system made it particularly appealing for scientific use and calculations. The Celsius scale was formerly known as the centigrade scale, reflecting the 100 divisions between the freezing and boiling points of water.
The Conversion Formula: The formula to convert Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C) is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula accounts for the different zero points and the different sizes of the degree intervals on the two scales. Subtracting 32 adjusts for the difference in zero points (freezing point of water is 32°F and 0°C), and multiplying by 5/9 adjusts for the different degree sizes (a Celsius degree is larger than a Fahrenheit degree).
Applying the Formula to 85°F: Let's calculate the Celsius equivalent of 85 degrees Fahrenheit:
°C = (85 - 32) × 5/9 °C = 53 × 5/9 °C = 265/9 °C ≈ 29.4
Therefore, 85 degrees Fahrenheit is approximately 29.4 degrees Celsius.
Why the Difference? The primary reason for the difference between Fahrenheit and Celsius lies in their historical development and the reference points used to define them. Fahrenheit's scale was initially based on somewhat arbitrary reference points, while Celsius was designed with the freezing and boiling points of water in mind, making it more directly related to a fundamental property of water. This direct relationship with water's phase transitions makes Celsius particularly useful in scientific contexts. Furthermore, the decimal-based nature of Celsius aligns well with the metric system, which is used in most scientific and international applications.
Kelvin: The Absolute Scale: While Fahrenheit and Celsius are the most commonly used temperature scales in everyday life, the Kelvin scale is the standard unit of temperature in scientific contexts. The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning that its zero point (0 K) is absolute zero – the theoretical temperature at which all atomic and molecular motion ceases. The size of one Kelvin is the same as the size of one degree Celsius, but the Kelvin scale is offset so that 0°C is equal to 273.15 K. This means that to convert from Celsius to Kelvin, you simply add 273.15. The Kelvin scale is particularly useful in scientific calculations because it avoids the use of negative temperatures, which can simplify equations and prevent errors.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the fundamental principles of temperature measurement and conversion remain constant, there are ongoing developments in the technology used to measure and monitor temperature. Digital thermometers, infrared thermometers, and thermal imaging cameras have become increasingly sophisticated, providing more accurate and detailed temperature readings in a variety of applications.
Digital Thermometers: Traditional mercury thermometers are gradually being replaced by digital thermometers, which offer several advantages, including greater accuracy, faster readings, and the absence of toxic mercury. Digital thermometers use electronic sensors called thermistors to measure temperature and display the results on a digital screen. These devices are widely used in healthcare, food safety, and environmental monitoring.
Infrared Thermometers: Infrared thermometers measure temperature by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object. These thermometers are non-contact, making them ideal for measuring the temperature of moving objects, hazardous materials, or surfaces that are difficult to reach. Infrared thermometers are used in a wide range of applications, including industrial process control, building inspection, and medical screening. During the COVID-19 pandemic, infrared thermometers became a common sight for quickly screening individuals for fever.
Thermal Imaging Cameras: Thermal imaging cameras create images based on the infrared radiation emitted by objects. These cameras can detect subtle temperature differences and display them as variations in color. Thermal imaging cameras are used in a variety of applications, including building inspection (to identify areas of heat loss or insulation problems), medical diagnostics (to detect inflammation or circulatory problems), and security surveillance (to detect people or objects in low-light conditions).
Smart Thermostats and Climate Control: The rise of smart home technology has led to the development of smart thermostats and climate control systems that can automatically adjust temperature settings based on occupancy, weather conditions, and user preferences. These systems use machine learning algorithms to optimize energy efficiency and improve comfort. They often integrate with other smart home devices and can be controlled remotely via smartphone apps. This integration allows for precise temperature management and significant energy savings.
Data-Driven Insights: The Internet of Things (IoT) is generating vast amounts of temperature data from sensors embedded in buildings, vehicles, and industrial equipment. This data can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize performance, and predict potential problems. For example, temperature sensors in data centers can be used to monitor the cooling systems and prevent overheating, while temperature sensors in refrigerated trucks can ensure that perishable goods are kept at the correct temperature during transport. The ability to collect and analyze temperature data in real-time is transforming industries and enabling new levels of efficiency and control.
Tips and Expert Advice
Converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius can be made easier with a few practical tips and tricks. Understanding the relationship between the scales and employing some mental shortcuts can help you quickly estimate temperatures without relying on a calculator.
Mental Math Shortcuts: While the exact conversion formula is essential for accurate calculations, you can use mental math shortcuts for quick estimations. Here's a simple method:
- Subtract 30 from the Fahrenheit temperature.
- Divide the result by 2.
This shortcut provides a reasonably close approximation, especially for temperatures in the typical range of human comfort. For example, let's apply this to 85°F:
- 85 - 30 = 55
- 55 / 2 = 27.5
This estimation (27.5°C) is close to the accurate conversion of 29.4°C. This shortcut is especially useful when you need a quick estimate without access to a calculator.
Common Temperature Benchmarks: Familiarizing yourself with some common temperature benchmarks in both Fahrenheit and Celsius can provide a valuable frame of reference. For instance:
- Freezing point of water: 32°F = 0°C
- Room temperature: 72°F = 22°C
- Normal human body temperature: 98.6°F = 37°C
- Boiling point of water: 212°F = 100°C
Knowing these benchmarks allows you to quickly gauge the relative warmth or coldness of a given temperature in either scale. For example, if you know that room temperature is around 22°C, you can easily estimate that 25°C is slightly warmer.
Context is Key: When interpreting temperature readings, it's important to consider the context. A temperature of 25°C (77°F) might be comfortable indoors but feel quite warm outdoors on a sunny day due to the effects of solar radiation. Similarly, a temperature of 10°C (50°F) might feel cold and damp in a coastal area but relatively mild in a dry desert climate. Factors like humidity, wind, and sunlight can significantly affect how a particular temperature is perceived.
Using Online Converters and Apps: While understanding the conversion formula is valuable, online converters and smartphone apps can provide quick and accurate conversions. Numerous websites and apps offer temperature conversion tools that allow you to instantly convert between Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin. These tools are particularly useful when you need precise conversions or are dealing with temperatures outside the typical range.
Understanding Significant Digits: When performing temperature conversions, it's important to pay attention to significant digits. The number of significant digits in the converted temperature should not exceed the number of significant digits in the original temperature. For example, if you are converting 85°F (two significant digits) to Celsius, the result should be rounded to two significant digits as well (29°C). This ensures that the converted temperature reflects the precision of the original measurement.
FAQ
Q: Why is Fahrenheit still used in the United States? A: The continued use of Fahrenheit in the United States is largely due to historical inertia and cultural familiarity. While the metric system, including Celsius, is widely used in science and industry in the U.S., the general public is more accustomed to Fahrenheit for everyday temperature readings.
Q: Is Celsius a metric unit? A: Yes, Celsius is considered a metric unit, although the base unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI) is the Kelvin. The Celsius scale is derived from the Kelvin scale and is widely used in conjunction with other metric units.
Q: What is absolute zero in Fahrenheit? A: Absolute zero, the theoretical lowest possible temperature, is approximately -459.67°F. This corresponds to 0 Kelvin or -273.15°C.
Q: How accurate are online temperature converters? A: Online temperature converters are generally very accurate, as they use the precise conversion formulas. However, it's always a good idea to double-check the results and ensure that the converter is using the correct formula and units.
Q: Can I convert temperatures in my head? A: Yes, with practice and the use of mental math shortcuts, you can become quite proficient at estimating temperature conversions in your head. Familiarizing yourself with common temperature benchmarks and using simple approximations can help you quickly gauge the relative warmth or coldness of a given temperature.
Conclusion
Converting 85 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius yields approximately 29.4 degrees Celsius, a comfortable temperature for many activities. More than just a number, this conversion highlights the importance of understanding different measurement systems in a globalized world. Whether you're planning a trip, conducting scientific research, or simply trying to understand the weather forecast, the ability to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a valuable skill.
Now that you've mastered the art of temperature conversion, take the next step! Share this article with your friends and family to spread the knowledge. Consider downloading a temperature conversion app or bookmarking an online converter for quick access. And, most importantly, be prepared to confidently discuss the weather in both Fahrenheit and Celsius, no matter where your adventures take you.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Two Main Eukaryotic Dna Polymerases That Extend Dna Are
Dec 05, 2025
-
Colonial Reaction To The Proclamation Of 1763
Dec 05, 2025
-
What Type Of Play Is Romeo And Juliet
Dec 05, 2025
-
What Causes A Reverse Sneeze In A Dog
Dec 05, 2025
-
The 4 Horsemen Of The Bible
Dec 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 85 Degrees F Is What C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.